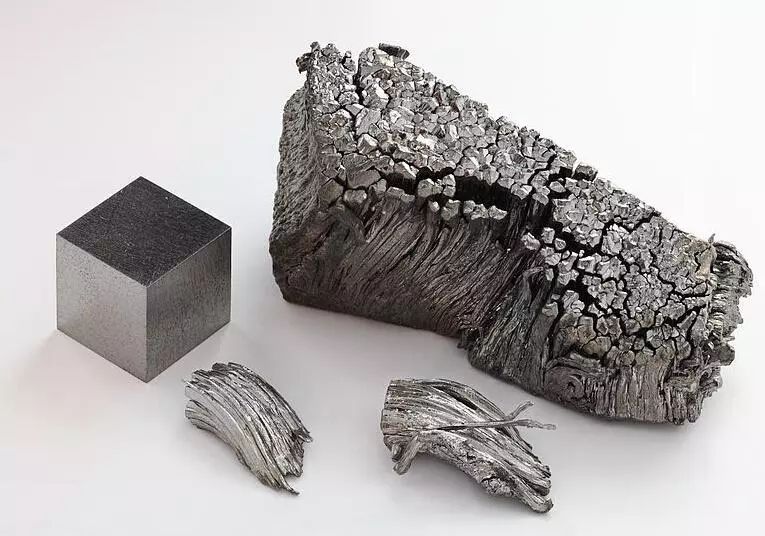
The atomic number of thulium element is 69 and its atomic weight is 168.93421. The content in the earth’s crust is two-thirds of 100000, which is the least abundant element among rare earth elements. It mainly exists in silico beryllium yttrium ore, black rare earth gold ore, phosphorus yttrium ore, and monazite. The mass fraction of rare earth elements in monazite generally reaches 50%, with thulium accounting for 0.007%. The natural stable isotope is only thulium 169. Widely used in high-intensity power generation light sources, lasers, high-temperature superconductors, and other fields.
Discovering History
Discovered by: P.T. Cleve
Discovered in 1878
After Mossander separated erbium earth and terbium earth from yttrium earth in 1842, many chemists used spectral analysis to identify and determine that they were not pure oxides of an element, which encouraged chemists to continue separating them. After separating ytterbium oxide and scandium oxide from oxidized bait, Cliff separated two new elemental oxides in 1879. One of them was named thulium to commemorate Cliff’s homeland in the Scandinavian Peninsula (Thulia), with the element symbol Tu and now Tm. With the discovery of thulium and other rare earth elements, the other half of the third stage of rare earth element discovery has been completed.
Electron configuration
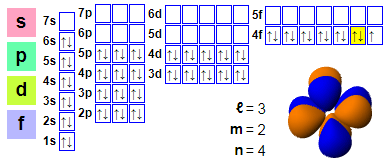
Electron configuration
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6 5s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f13
Thulium is a silver white metal with ductility and can be cut open with a knife due to its soft texture; Melting point 1545 ° C, boiling point 1947 ° C, density 9.3208.
Thulium is relatively stable in air; Thulium oxide is a light green crystal. Salt (divalent salt) oxides are all light green in color.
Application
Although thulium is quite rare and expensive, it still has some applications in special fields.
High intensity discharge light source
Thulium is often introduced into high-intensity discharge light sources in the form of high-purity halides (usually thulium bromide), with the aim of utilizing the spectrum of thulium.
Laser
Three doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Ho: Cr: Tm: YAG) solid-state pulse laser can be produced by using thulium ion, chromium ion, and holmium ion in yttrium aluminum garnet, which can emit a wavelength of 2097 nm; It is widely used in military, medical, and meteorological fields. The wavelength of the laser emitted by the thulium doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Tm: YAG) solid-state pulse laser ranges from 1930 nm to 2040 nm. Ablation on the surface of tissues is very effective, as it can prevent clotting from becoming too deep in both air and water. This makes thulium lasers have great potential for application in basic laser surgery. Thulium laser is very effective in ablating tissue surfaces due to its low energy and penetrating power, and can coagulate without causing deep wounds. This makes thulium lasers have great potential for application in laser surgery
Thulium doped laser
X-ray source
Despite the high cost, portable X-ray devices containing thulium have begun to be widely used as radiation sources in nuclear reactions. These radiation sources have a lifespan of about one year and can be used as medical and dental diagnostic tools, as well as defect detection tools for mechanical and electronic components that are difficult to reach by manpower. These radiation sources do not require significant radiation protection – only a small amount of lead is required. The application of thulium 170 as a radiation source for close range cancer treatment is becoming increasingly widespread. This isotope has a half-life of 128.6 days and five emission lines of considerable intensity (7.4, 51.354, 52.389, 59.4, and 84.253 kiloelectron volts). Thulium 170 is also one of the four most commonly used industrial radiation sources.
High temperature superconducting materials
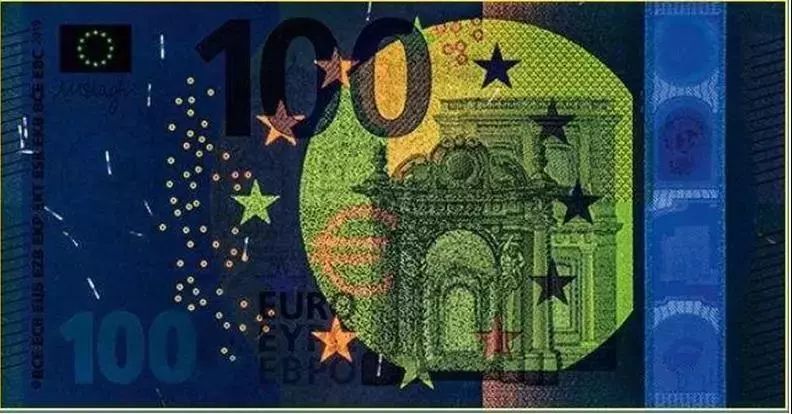
Similar to yttrium, thulium is also used in high-temperature superconductors. Thulium has potential use value in ferrite as a ceramic magnetic material used in microwave equipment. Due to its unique spectrum, thulium can be applied to arc lamp lighting like scandium, and the green light emitted by arc lamps using thulium will not be covered by the emission lines of other elements. Due to its ability to emit blue fluorescence under ultraviolet radiation, thulium is also used as one of the anti-counterfeiting symbols in euro banknotes. The blue fluorescence emitted by calcium sulfate added with thulium is used in personal dosimetry for radiation dose detection.
Other applications
Due to its unique spectrum, thulium can be applied in arc lamp lighting like scandium, and the green light emitted by arc lamps containing thulium will not be covered by the emission lines of other elements.
Thulium emits blue fluorescence under ultraviolet radiation, making it one of the anti-counterfeiting symbols in euro banknotes.
Euro under UV irradiation, with clear anti-counterfeiting markings visible
Post time: Aug-25-2023



