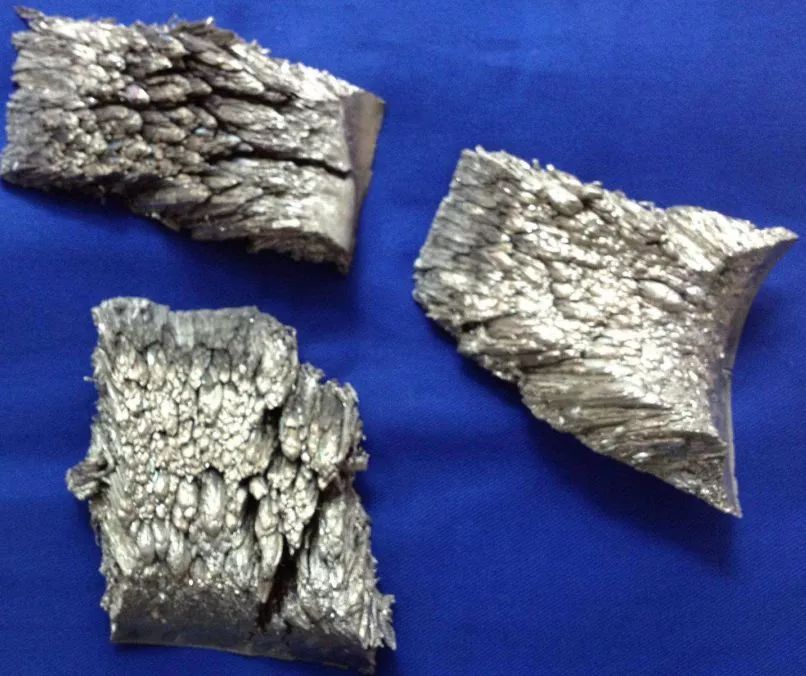
Scandium, with element symbol Sc and Atomic number of 21, is easily soluble in water, can interact with hot water, and easily darkens in the air. Its main valence is+3. It is often mixed with gadolinium, erbium, and other elements, with a low yield and a content of approximately 0.0005% in the crust. Scandium is often used to make special glass and lightweight high-temperature alloys.
At present, the proven reserves of scandium in the world are only 2 million tons, 90~95% of which are contained in Bauxite, phosphorite and iron titanium ores, and a small part in uranium, thorium, tungsten and rare earth ores, mainly distributed in Russia, China, Tajikistan, Madagascar, Norway and other countries. China is very rich in scandium resources, with huge mineral reserves related to scandium. According to incomplete statistics, the reserves of scandium in China are about 600000 tons, which are contained in Bauxite and phosphorite deposits, porphyry and quartz vein tungsten deposits in South China, rare earth deposits in South China, Bayan Obo rare earth iron ore deposit in Inner Mongolia, and Panzhihua vanadium titanium magnetite deposit in Sichuan.
Due to the scarcity of scandium, the price of scandium is also very high, and at its peak, the price of scandium was inflated to 10 times the price of gold. Although the price of scandium has fallen, it is still four times the price of gold!
Discovering History
In 1869, Mendeleev noticed a gap in atomic mass between calcium (40) and titanium (48), and predicted that there was also an undiscovered intermediate atomic mass element here. He predicted that its oxide is X ₂ O Å. Scandium was discovered in 1879 by Lars Frederik Nilson of Uppsala University in Sweden. He extracted it from the black rare gold mine, a complex ore that contains 8 types of metal oxides. He has extracted Erbium(III) oxide from black rare gold ore, and obtained Ytterbium(III) oxide from this oxide, and there is another oxide of lighter element, whose spectrum shows that it is an unknown metal. This is the metal predicted by Mendeleev, whose oxide is Sc₂O₃. The scandium metal itself was produced from Scandium chloride by electrolytic melting in 1937.
Mendeleev
Electron configuration
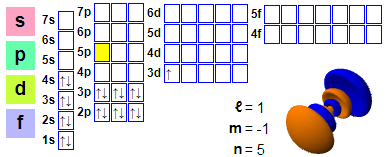
Electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1
Scandium is a soft, silver white transition metal with a melting point of 1541 ℃ and a boiling point of 2831 ℃.
For a considerable period of time after its discovery, the use of scandium was not demonstrated due to its difficulty in production. With the increasing improvement of rare earth element separation methods, there is now a mature process flow for purifying scandium compounds. Because scandium is less alkaline than yttrium and Lanthanide, the hydroxide is the weakest, so the rare earth element mixed mineral containing scandium will be separated from the rare earth element by “step precipitation ” method when Scandium(III) hydroxide is treated with ammonia after being transferred into solution. The other method is to separate Scandium nitrate by Polar decomposition of nitrate. Because scandium nitrate is the easiest to decompose, scandium can be separated. In addition, the comprehensive recovery of accompanying scandium from uranium, thorium, tungsten, tin and other mineral deposits is also an important source of scandium.
After obtaining a pure scandium compound, it is converted into ScCl Å and co melted with KCl and LiCl. The molten zinc is used as the cathode for electrolysis, causing scandium to precipitate on the zinc electrode. Then, the zinc is evaporated to obtain metallic scandium. This is a lightweight silver white metal with very active chemical properties, which can react with hot water to generate hydrogen gas. So the metal scandium you see in the picture is sealed in a bottle and protected with argon gas, otherwise scandium will quickly form a dark yellow or gray oxide layer, losing its shiny metallic luster.
Applications
Lighting industry
The uses of scandium are concentrated in very bright directions, and it is not an exaggeration to call it the Son of Light. The first magic weapon of scandium is called scandium sodium lamp, which can be used to bring light to thousands of households. This is a metal halide Electric light: the bulb is filled with Sodium iodide and Scandium triiodide, and scandium and sodium foil are added at the same time. During high-voltage discharge, scandium ions and sodium ions respectively emit light of their characteristic emission wavelengths. The spectral lines of sodium are 589.0 and 589.6 nm, two famous yellow lights, while the spectral lines of scandium are 361.3~424.7 nm, a series of near ultraviolet and blue light emissions. Because they complement each other, the overall light color produced is white light. It is precisely because scandium sodium lamps have the characteristics of high luminous efficiency, good light color, power saving, long service life, and strong fog breaking ability that they can be widely used for television cameras, squares, sports venues, and road lighting, and are known as the third generation light sources. In China, this type of lamp is gradually being promoted as a new technology, while in some developed countries, this type of lamp was widely used as early as the early 1980s.
The second magic weapon of scandium is solar photovoltaic cells, which can collect the light scattered on the ground and turn it into electricity to drive human society. Scandium is the best barrier metal in metal insulator semiconductor silicon solar cells and solar cells.
Its third magic weapon is called γ A ray source, this magic weapon can shine brightly on its own, but this kind of light cannot be received by the naked eye, it is a high-energy photon flow. We usually extract 45Sc from minerals, which is the only Natural isotopes of scandium. Each 45Sc nucleus contains 21 protons and 24 neutrons. 46Sc, an artificial radioactive isotope, can be used as γ Radiation sources or tracer atoms can also be used for radiotherapy of malignant tumors. There are also applications like yttrium gallium scandium garnet laser, Scandium fluoride glass infrared Optical fiber, and scandium coated cathode ray tube on television. It seems that scandium is born with brightness.
Alloy industry
Scandium in its elemental form has been widely used for doping aluminum alloys. As long as a few thousandths of scandium is added to aluminum, a new Al3Sc phase will be formed, which will play a Metamorphism role in aluminum alloy and make the structure and properties of the alloy change significantly. Adding 0.2%~0.4% Sc (which is really similar to the proportion of adding salt to stir fried vegetables at home, only a little bit is needed) can increase the recrystallization temperature of the alloy by 150-200 ℃, and significantly improve high-temperature strength, structural stability, welding performance, and corrosion resistance. It can also avoid the embrittlement phenomenon that is easy to occur during long-term work at high temperatures. High strength and high toughness aluminum alloy, new high-strength corrosion-resistant weldable aluminum alloy, new high-temperature aluminum alloy, high-strength neutron irradiation resistant aluminum alloy, etc., have very attractive development prospects in aerospace, aviation, ships, nuclear reactors, light vehicles and high-speed trains.
Scandium is also an excellent modifier for iron, and a small amount of scandium can significantly improve the strength and hardness of cast iron. In addition, scandium can also be used as an additive for high-temperature tungsten and chromium alloys. Of course, in addition to making wedding clothes for others, scandium has a high melting point and its density is similar to aluminum, and is also used in high melting point lightweight alloys such as scandium titanium alloy and scandium magnesium alloy. However, due to its high price, it is generally only used in high-end manufacturing industries such as space shuttles and rockets.
Ceramic material
Scandium, a single substance, is generally used in alloys, and its oxides play an important role in ceramic materials in a similar way. The tetragonal zirconia ceramic material, which can be used as an electrode material for solid oxide fuel cells, has a unique property where the conductivity of this electrolyte increases with increasing temperature and oxygen concentration in the environment. However, the crystal structure of this ceramic material itself cannot exist stably and has no industrial value; It is necessary to doping some substances that can fix this structure in order to maintain its original properties. Adding 6~10% Scandium oxide is like a concrete structure, so that zirconia can be stabilized on a square lattice.
There are also engineering ceramic materials such as high-strength and high-temperature resistant silicon nitride as densifiers and stabilizers.
As a densifier, Scandium oxide can form a refractory phase Sc2Si2O7 at the edge of fine particles, thus reducing the high-temperature deformation of engineering ceramics. Compared with other oxides, it can better improve the high-temperature mechanical properties of silicon nitride.
Catalytic chemistry
In chemical engineering, scandium is often used as a catalyst, while Sc2O3 can be used for dehydration and deoxidation of ethanol or isopropanol, decomposition of acetic acid, and production of ethylene from CO and H2. The Pt Al catalyst containing Sc2O3 is also an important catalyst for heavy oil hydrogenation purification and refining processes in petrochemical industry. In catalytic cracking reactions such as Cumene, the activity of Sc-Y zeolite catalyst is 1000 times higher than that of Aluminium silicate catalyst; Compared with some traditional catalysts, the development prospects of scandium catalysts will be very bright.
Nuclear energy industry
Adding a small amount of Sc2O3 to UO2 in high-temperature reactor nuclear fuel can avoid lattice transformation, volume increase, and cracking caused by UO2 to U3O8 conversion.
Fuel cell
Similarly, adding 2.5% to 25% scandium to nickel alkali batteries will increase their service life.
Agricultural breeding
In agriculture, seeds such as corn, beet, pea, wheat and sunflower can be treated with Scandium sulfate (the concentration is generally 10-3~10-8mol/L, different plants will have different), and the actual effect of promoting germination has been achieved. After 8 hours, the dry weight of roots and buds increased by 37% and 78% respectively compared with seedlings, but the mechanism is still under study.
From Nielsen’s attention to the debt of Atomic mass data to today, scandium has entered people’s vision for only a hundred or twenty years, but it has almost sat on the bench for a hundred years. It was not until the vigorous development of material science in the late last century that it brought vitality to him. Today, rare earth elements, including scandium, have become hot stars in materials science, playing ever-changing roles in thousands of systems, bringing more convenience to our lives every day, and creating economic value that is even more difficult to measure.
Post time: Jun-29-2023